When managing large volumes of high-resolution satellite imagery (e.g., 1:10,000 scale sheets), visualizing coverage gaps becomes challenging due to performance limitations in ArcMap. This script automates the creation of vector polygons representing raster extents for efficient gap analysis.

Visualization: Red outlines = actual coverage, Green polygons = generated extents
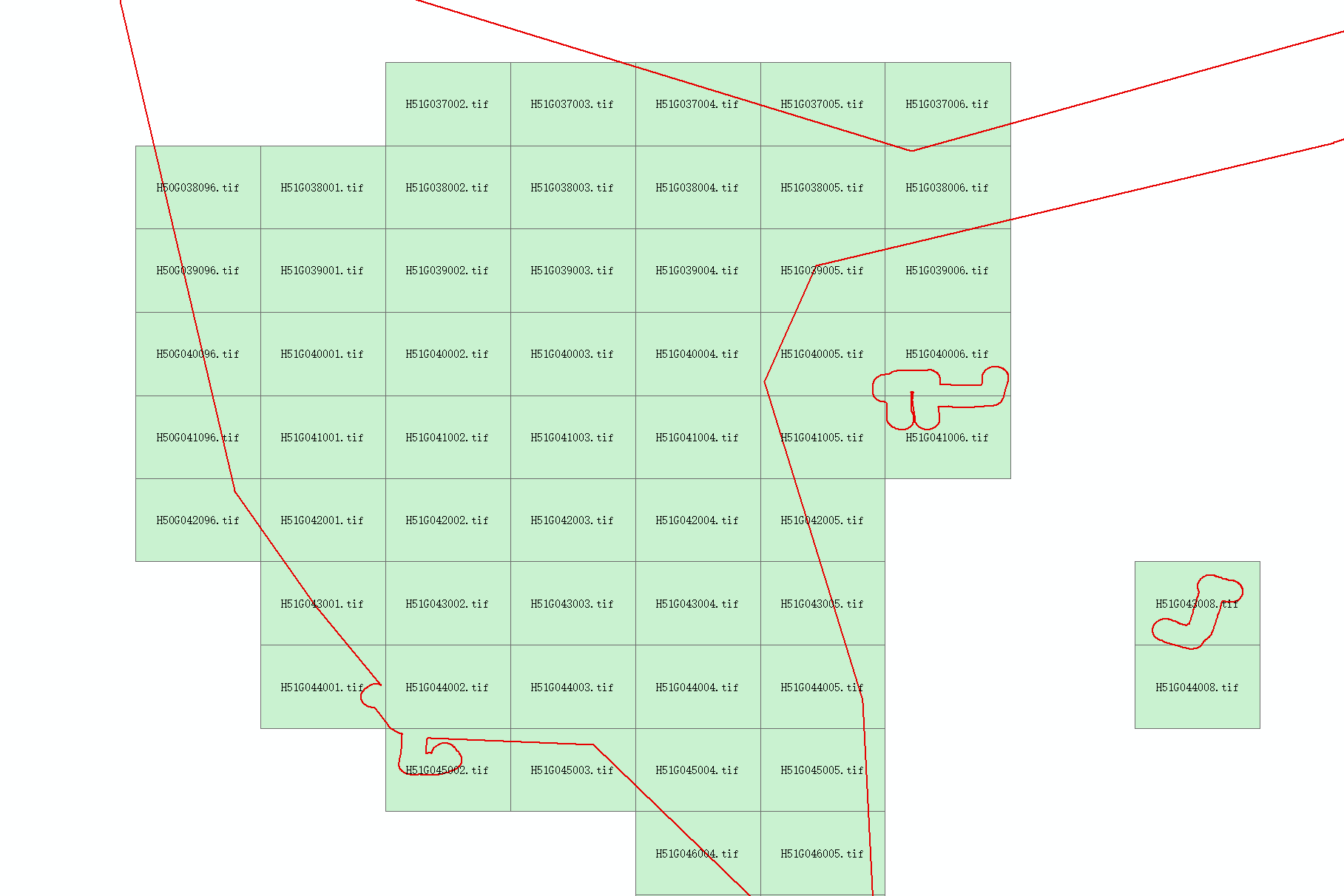
Detail showing alignment accuracy
Implementation Code
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import time
import arcpy
def create_directory(path):
"""Ensure directory exists, create if missing"""
if os.path.isdir(path):
if not os.path.exists(path):
os.makedirs(path)
else:
parent_dir = os.path.dirname(path)
if not os.path.exists(parent_dir):
os.makedirs(parent_dir)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Configure input/output
raster_directory = r'F:\gisData\data0929\refY202410072'
output_shapefile = os.path.join(raster_directory, 'shp', 'RasterExtent.shp')
start_time = time.time()
arcpy.env.workspace = raster_directory
raster_list = arcpy.ListRasters()
if not raster_list:
raise IOError("Error: No raster files found!")
# Prepare output feature class
if arcpy.Exists(output_shapefile):
arcpy.Delete_management(output_shapefile)
create_directory(output_shapefile)
output_fc = arcpy.CreateFeatureclass_management(
os.path.dirname(output_shapefile),
"RasterExtent.shp",
"POLYGON"
)
arcpy.AddField_management(output_fc, "RasterName", "TEXT", 50)
# Process rasters
with arcpy.da.InsertCursor(output_fc, ["SHAPE@", "RasterName"]) as cursor:
for raster_file in raster_list:
raster = arcpy.Raster(raster_file)
extent = raster.extent
# Construct polygon from extent
polygon_points = arcpy.Array([
arcpy.Point(extent.XMin, extent.YMin), # LL
arcpy.Point(extent.XMin, extent.YMax), # UL
arcpy.Point(extent.XMax, extent.YMax), # UR
arcpy.Point(extent.XMax, extent.YMin), # LR
arcpy.Point(extent.XMin, extent.YMin) # Close ring
])
cursor.insertRow([arcpy.Polygon(polygon_points), raster_file])
# Performance metrics
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
print(f"Process completed in: {elapsed:.2f} seconds")
Key Workflow
- Input Configuration: Specify directory containing raster files
- Output Handling: Automatically creates output shapefile
Extent Extraction:
- Retrieves XMin/YMin/XMax/YMax for each raster
- Constructs rectangular polygons from corner coordinates
- Attribute Storage: Preserves original raster filenames
Advantages
- Eliminates manual extent digitization
- Enables efficient coverage gap analysis
- Handles thousands of rasters in batch processing
- Integrates with standard ArcGIS workflows
Note: Requires ArcGIS Desktop with Spatial Analyst extension. Execution time scales linearly with raster count.