While developing a workflow involving spatial data duplication, an analyst requested help with client requirements:
① Convert individual polygons to WKT format in TXT files
② Merge multiple polygons into MultiPolygon WKT format

Understanding WKT
Well-known text (WKT) is a text markup language standardized by the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC) for representing:
- Vector geometries (points, linestrings, polygons)
- Coordinate reference systems
- Coordinate transformations
Solution via QGIS Plugin
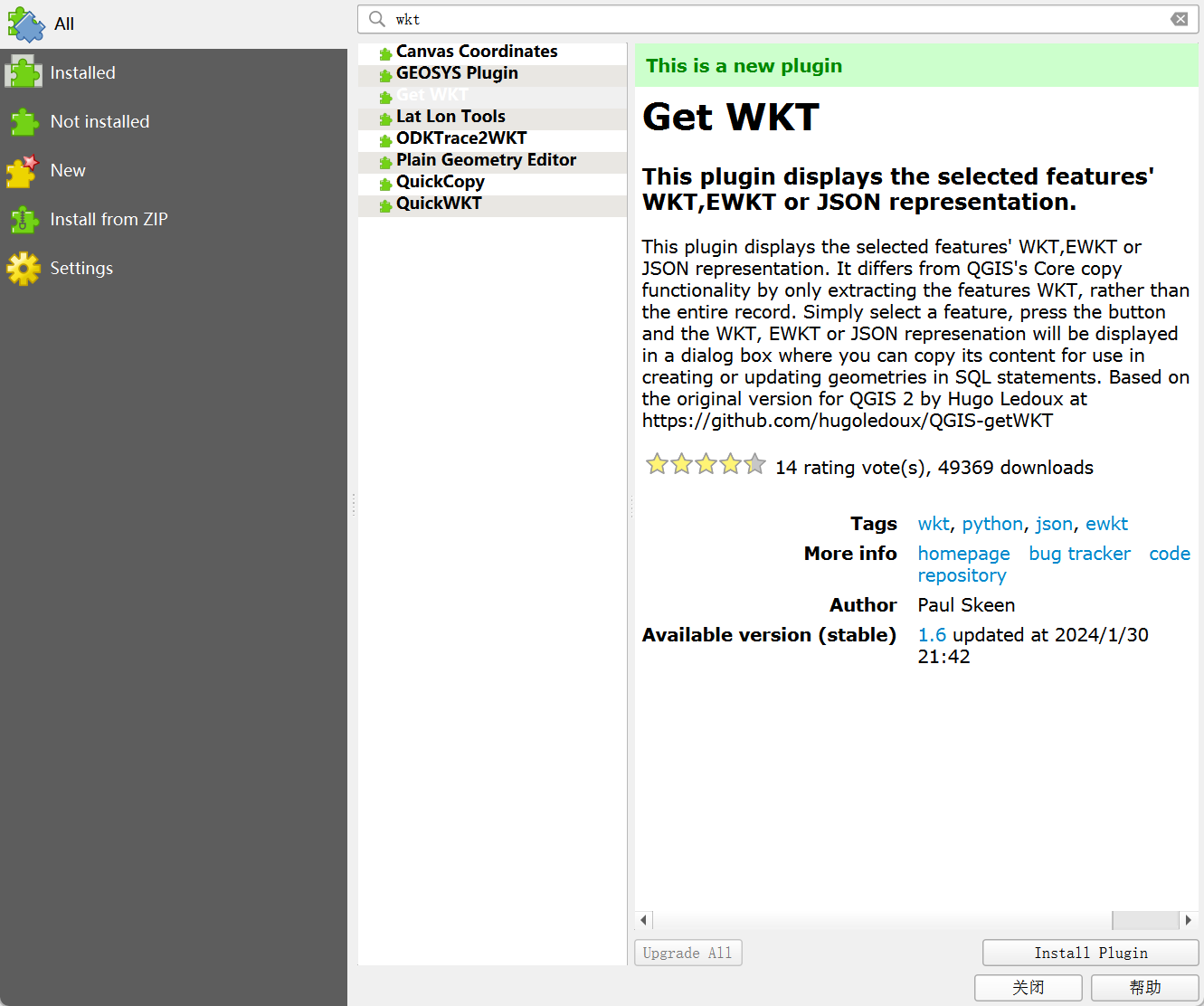
Step 1: Install Get WKT Plugin
- Navigate to:
Plugins → Manage and Install Plugins... - Search "WKT"
- Select "Get WKT" plugin
- Click
Install Plugin
Step 2: Export Single Feature WKT
- Load polygon data
- Select target feature
- Execute:
Plugins → Get WKT → Get WKT String - Copy output to TXT
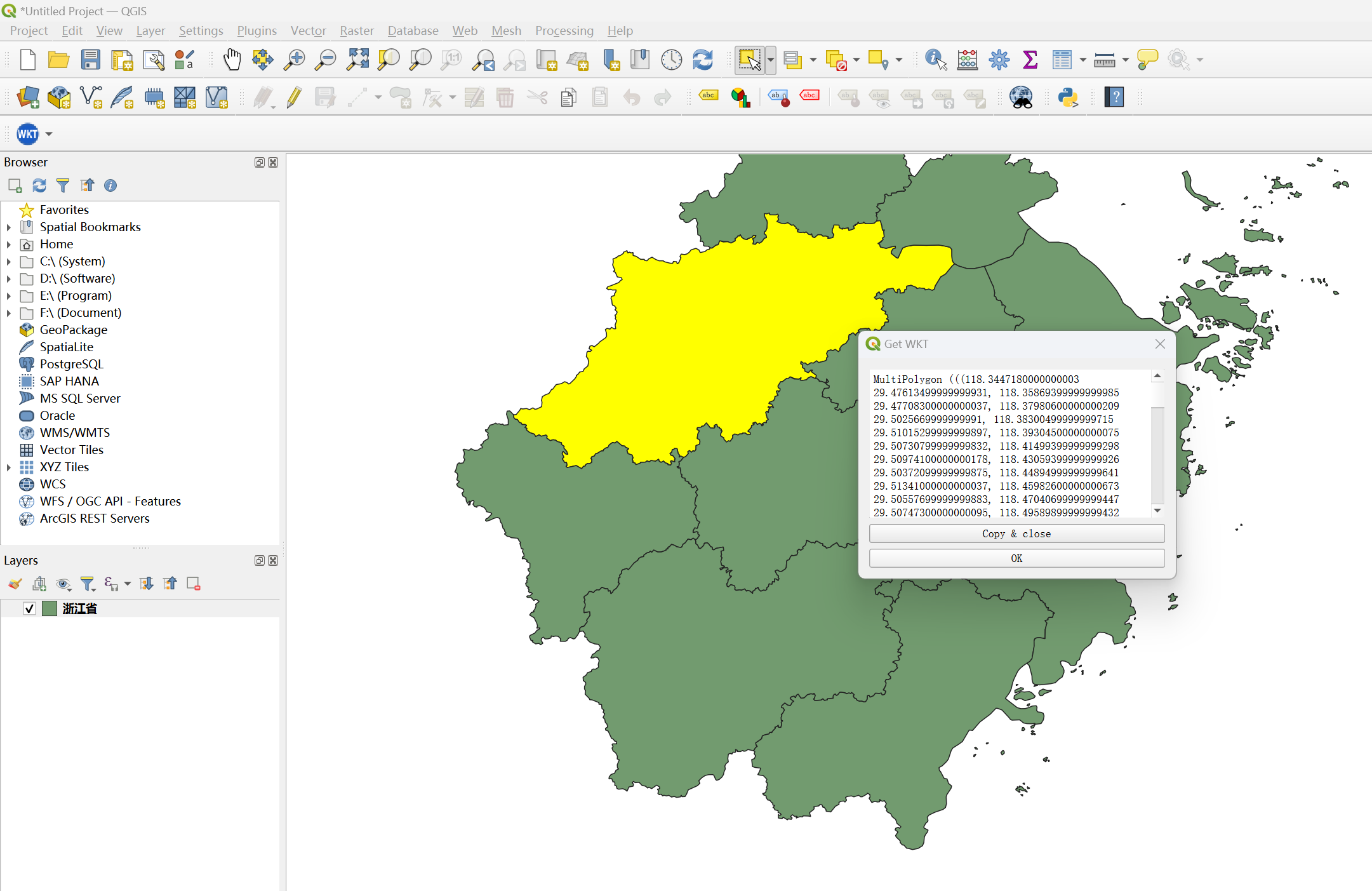
Limitation: Does not support multi-feature export
Python Script for MultiPolygon Conversion
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import datetime
from osgeo import ogr
from shapely.geometry import MultiPolygon
from shapely.wkt import loads
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Input/Output paths
in_shapefile = r"./data-use/shp/Guangdong.shp"
out_file = r'./results/Guangdong_' + datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y%m%d') + '.txt'
# Process shapefile
driver = ogr.GetDriverByName("ESRI Shapefile")
dataSource = driver.Open(in_shapefile, 0)
layer = dataSource.GetLayer()
# Aggregate polygons
polygons = []
for feature in layer:
geom = feature.GetGeometryRef().ExportToWkt()
polygons.append(loads(geom))
# Generate MultiPolygon WKT
multi_poly = MultiPolygon(polygons)
with open(out_file, 'w') as f:
f.write(multi_poly.wkt)Validation with QuickWKT Plugin
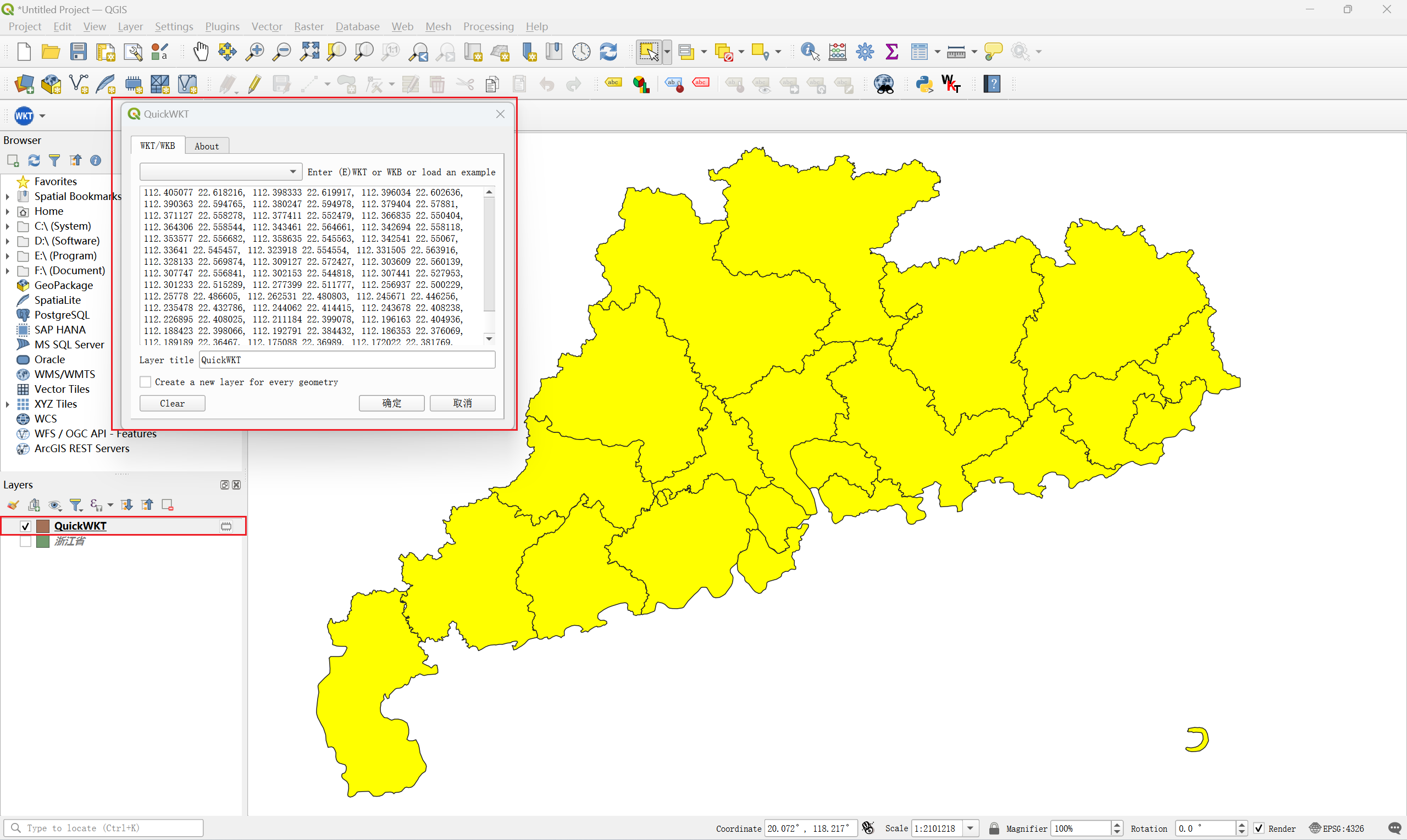
- Install "QuickWKT" plugin
- Paste generated WKT
- Verify unified MultiPolygon visualization