When crafting dynamic marathon routes from official maps, directly tracing simplified route images is inefficient without proper spatial referencing. Georeferencing solves this by aligning raster images with real-world coordinates.
Manual Georeferencing in QGIS
- Activate tool:
Layer → Georeferencer
- Load route image: Click
Add Raster
Add control points:
- Click identifiable features (e.g., road intersections)
- Map points to corresponding locations in reference basemap
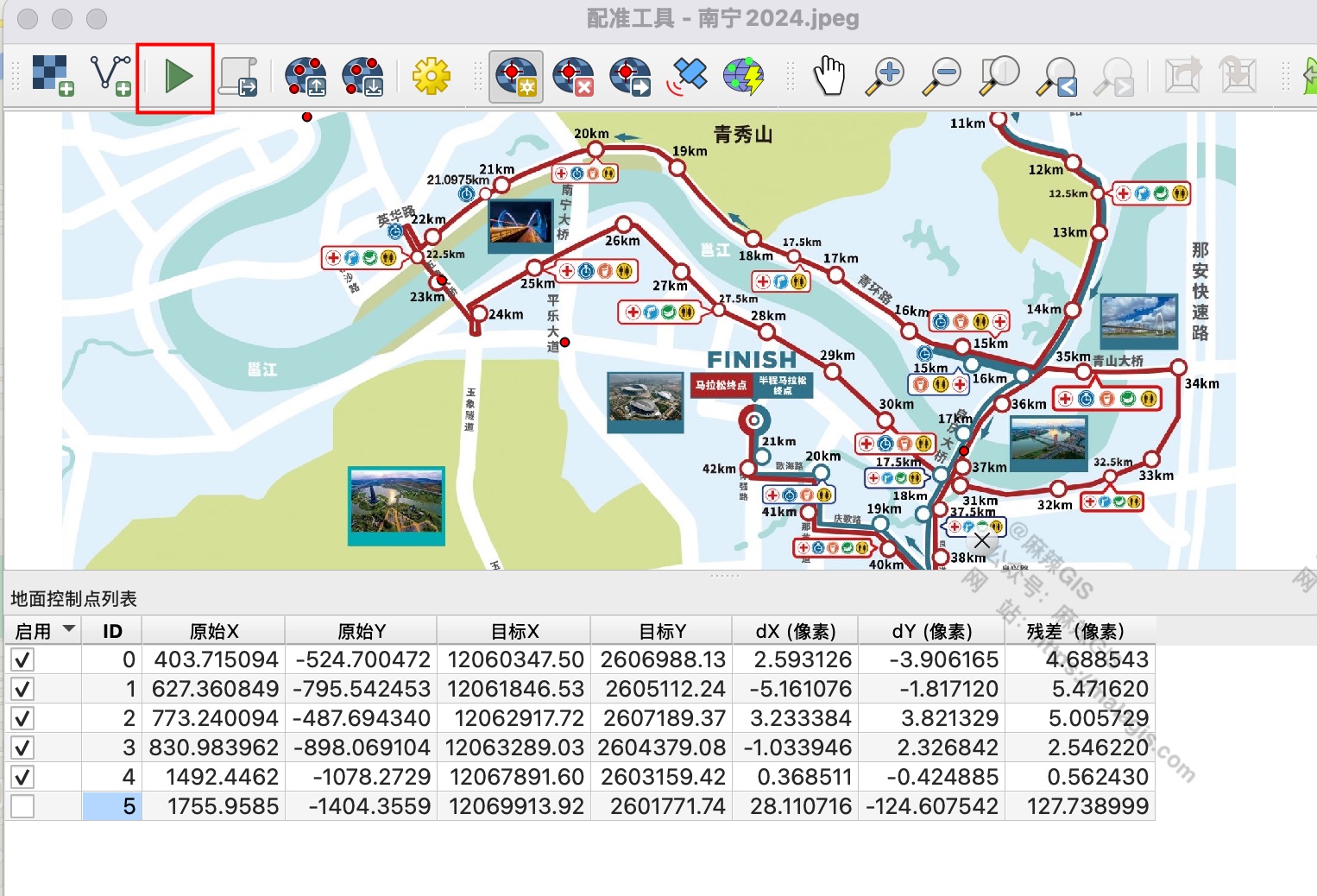
- Execute transformation:
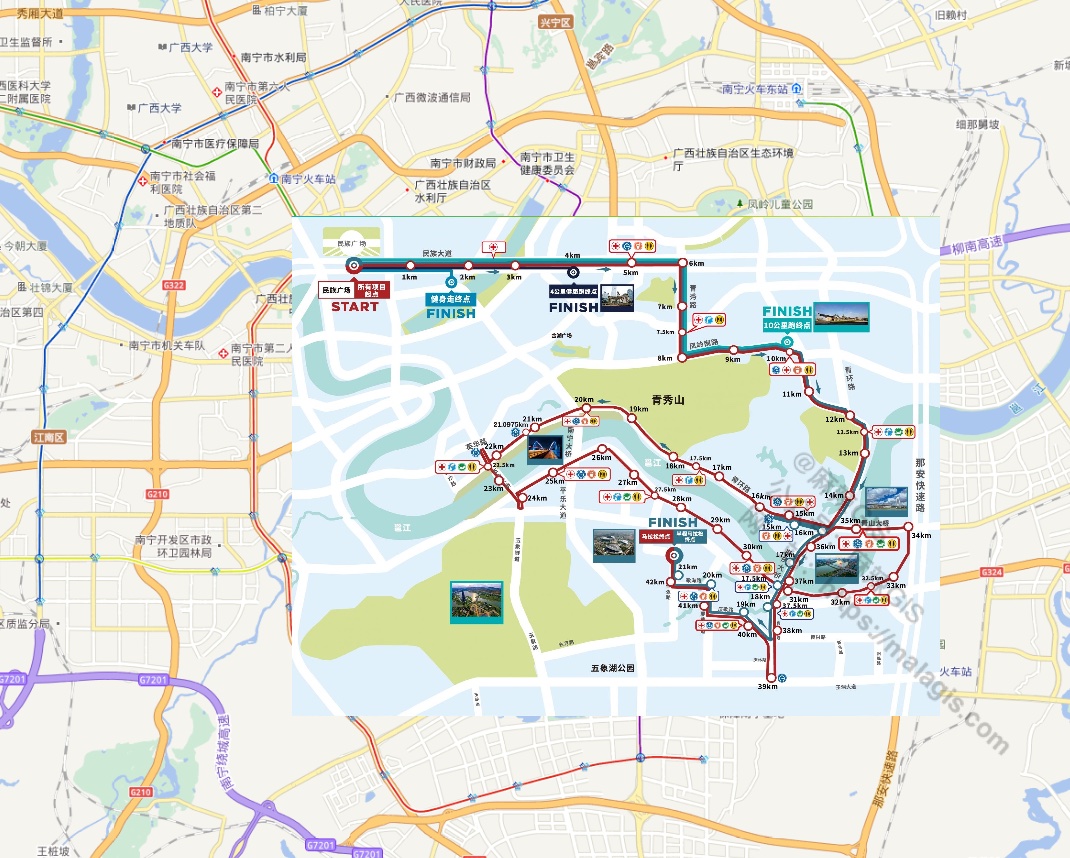
Note: Use 8-12 well-distributed points for acceptable accuracy.
AI-Powered Georeferencing with Bunting Labs Plugin
- Install AI Vectorizer plugin from Bunting Labs
- Load target image and reference basemap
- Align map canvas:
- Generate control points automatically:
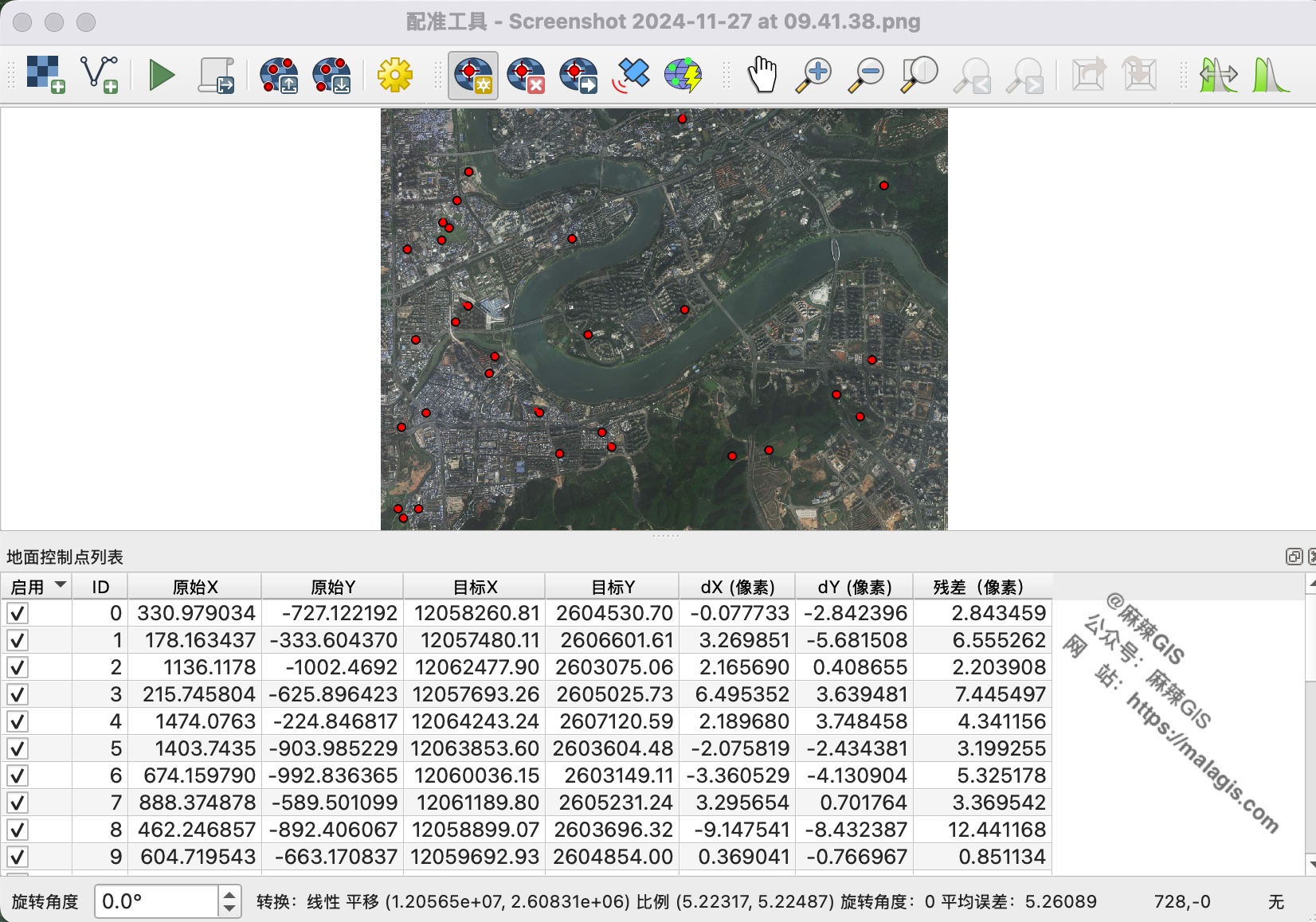
- Verify auto-generated points:
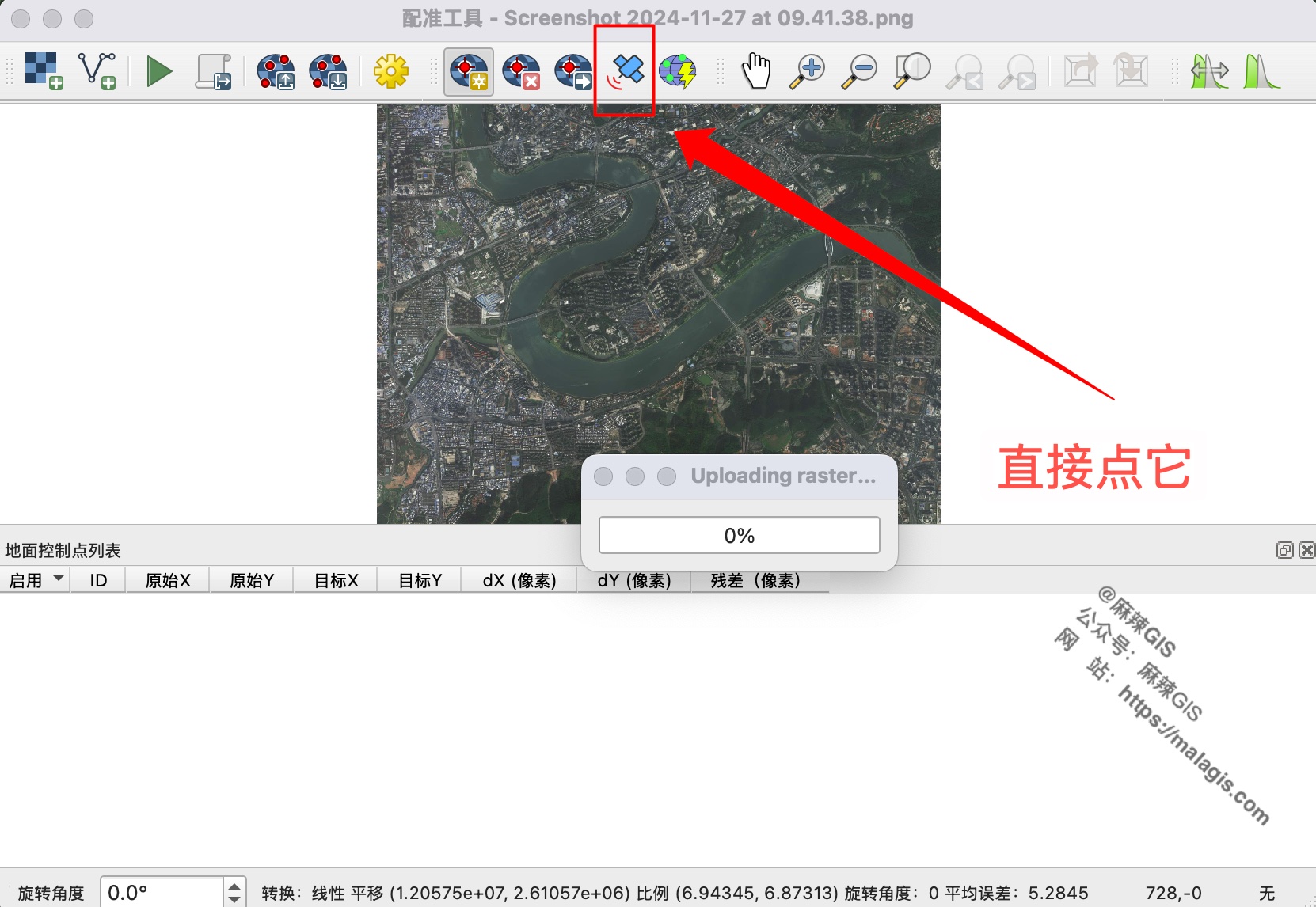
- Execute transformation:
Important Limitations:
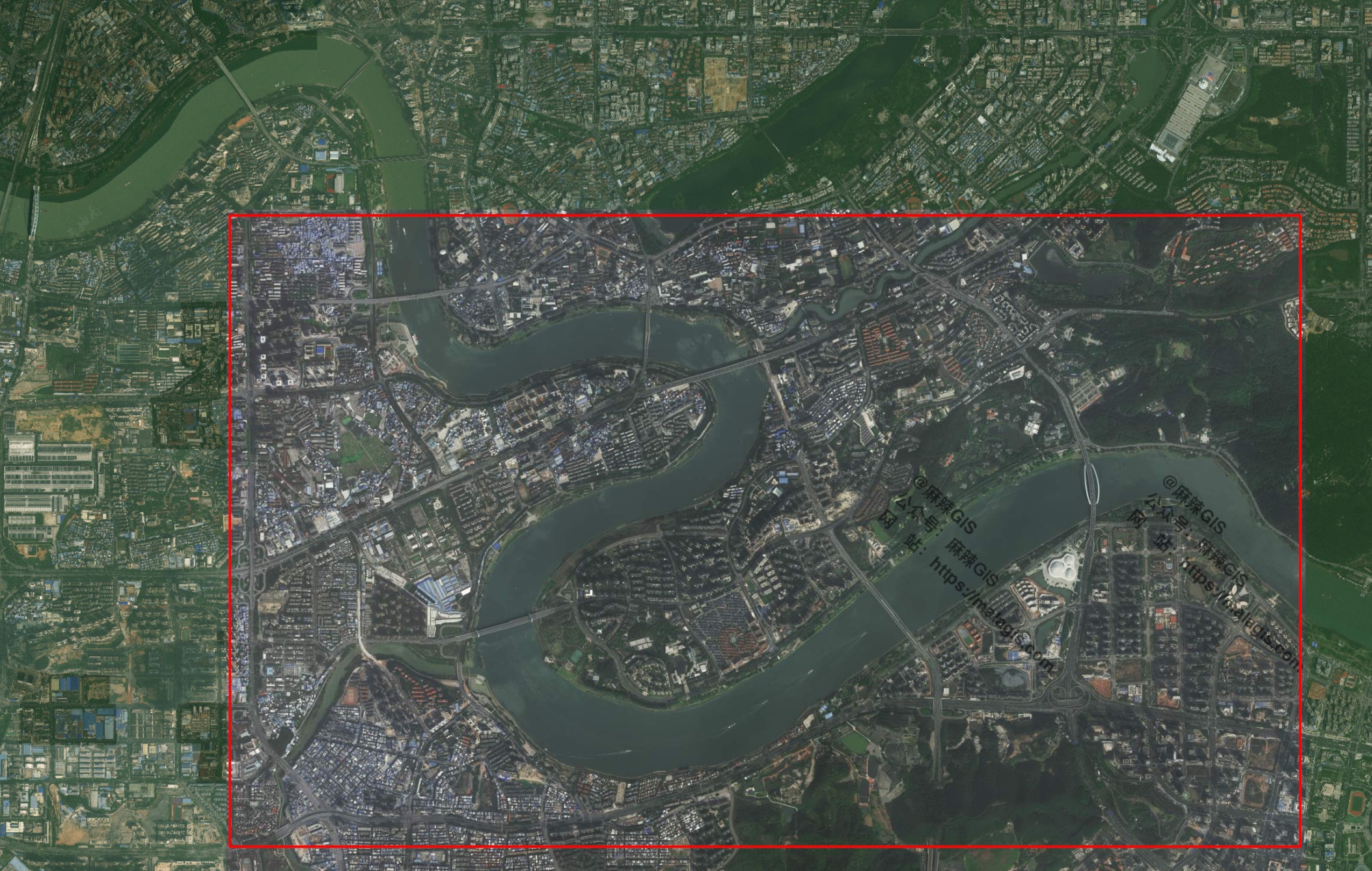
- AI excels with detailed satellite/map images
- Fails with simplified schematics:
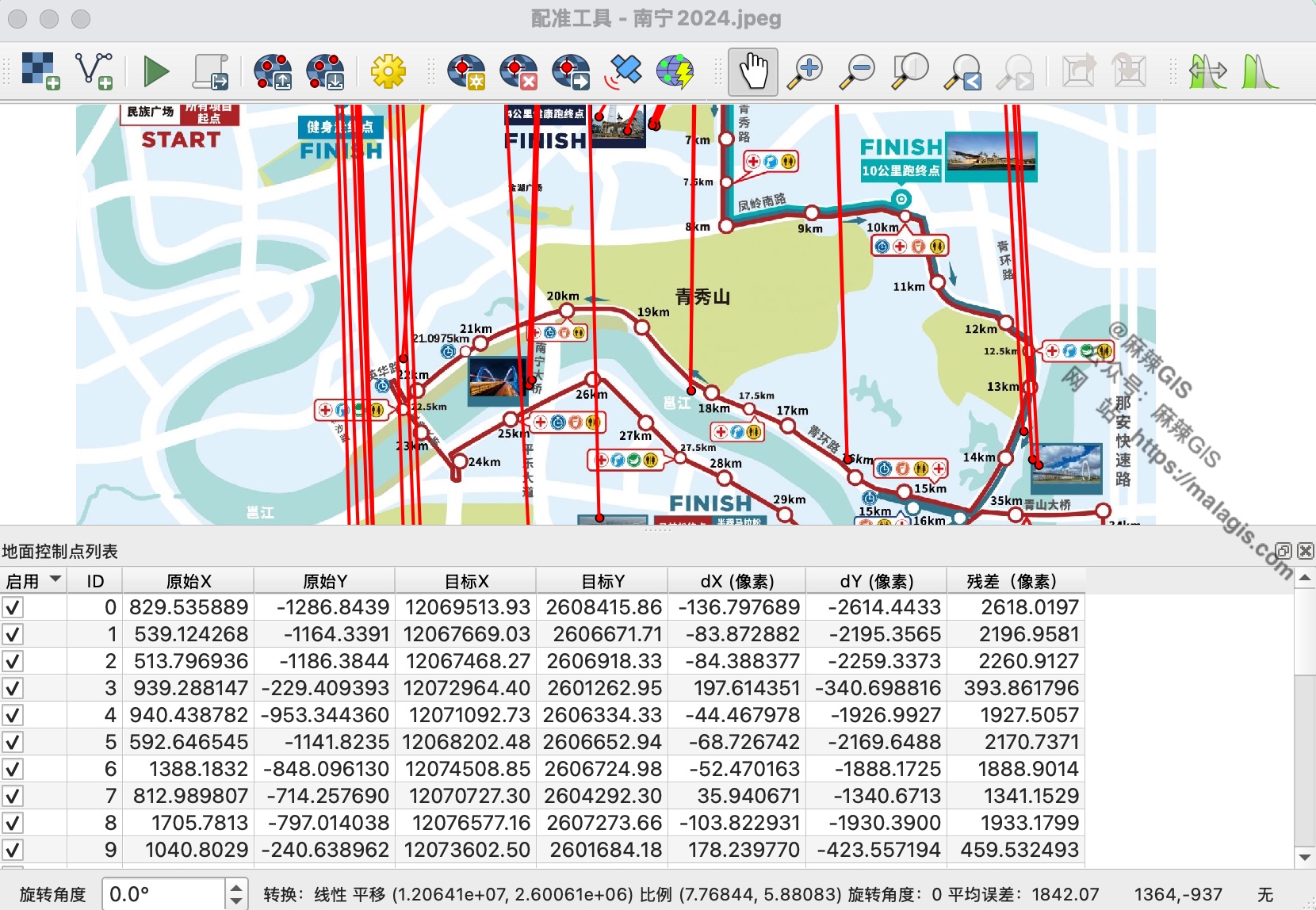
Technology Implications
While AI georeferencing accelerates workflows for standard maps, manual methods remain essential for stylized route diagrams. The evolution of GIS AI promises liberation from tedious tasks, yet raises questions about shifting professional skill requirements.
Previous tutorial: Creating Dynamic Marathon Route Visualizations with MapPlus: A No-Code GIS Solution - MalaGIS
